Fungal Rash Treatment in Lehi, Utah
Types of fungal rashes
Tinea Pedis
(Athlete's foot)
Tinea Pedis
A fungal infection primarily affecting the feet, often causing itching, scaling, and redness, particularly between the toes.
Tinea Corporis
(Ringworm)
Tinea Corporis
Presents as circular, scaly patches with raised borders, occurring on the body, excluding the scalp, groin, hands, and feet.
Tinea Versicolor
(Sun Fungus)
Tinea Versicolor
Characterized by discolored patches of skin, typically on the chest and back, resulting from an overgrowth of yeast that naturally lives on the skin.
Tinea Cruris
(Jock Itch)
Tinea Cruris
A fungal infection of the groin area, causing itching, redness, and a rash, more common in men and those who sweat heavily.
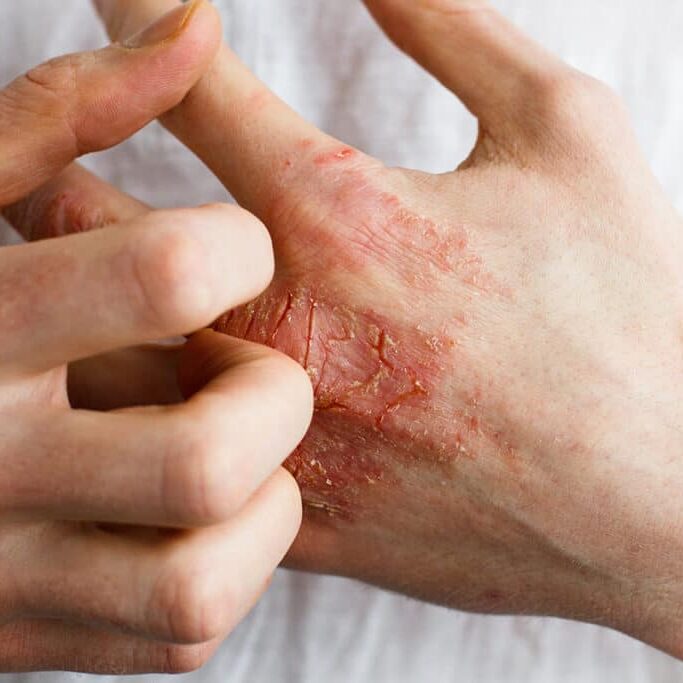
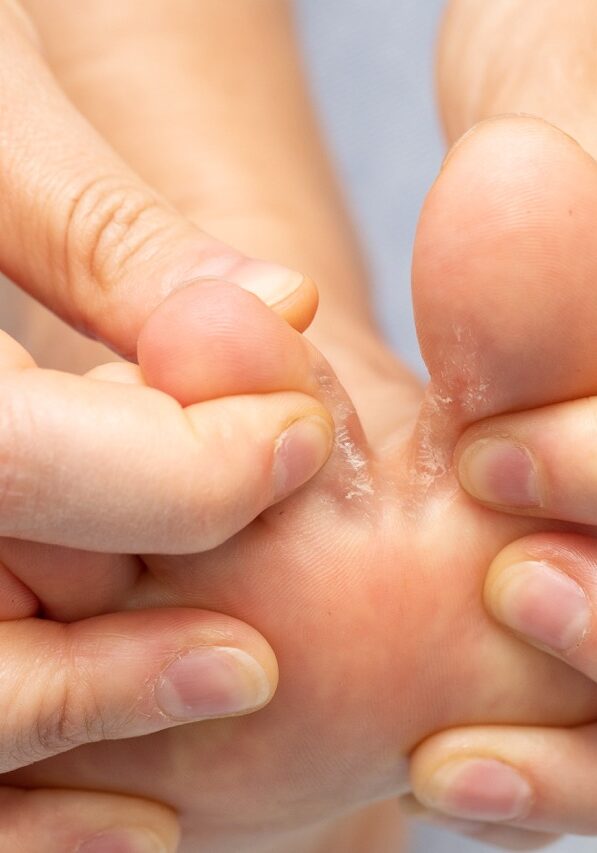
What is Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)?
What are the symptoms of Athlete's Foot?
-
Scaly, peeling, or cracked skin
This is a hallmark symptom, often occurring between the toes. It can also affect the soles and sides of the feet.
-
Itchiness
A persistent and often intense itching sensation is very common. Itching may be worse after removing shoes and socks.
-
Burning or stinging
The affected skin may experience a burning or stinging sensation.
-
Redness & inflammation
The skin can become red, and in people with darker skin tones, it may appear purplish or grayish.
-
Nail changes
If the infection spreads to the toenails, they may become discolored, thick, and brittle.
-
Blisters
In some cases, small blisters may develop, which can ooze or become crusty.
How to prevent Athlete's foot?
Preventing athlete's foot involves maintaining dry, clean feet. Thoroughly dry feet, especially between the toes, after showering or swimming. Wear breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks. Avoid walking barefoot in public areas like locker rooms. Wash your hands after touching your feet. People who live in a warm climate are at higher risk
Treatment options for Athlete's foot?
Over-the-counter antifungal creams can often handle mild cases. For more stubborn cases, we may prescribe stronger prescription-strength topical or oral antifungal medications. Remember, proper foot care, including regular washing and thorough drying, is essential for long-term success.
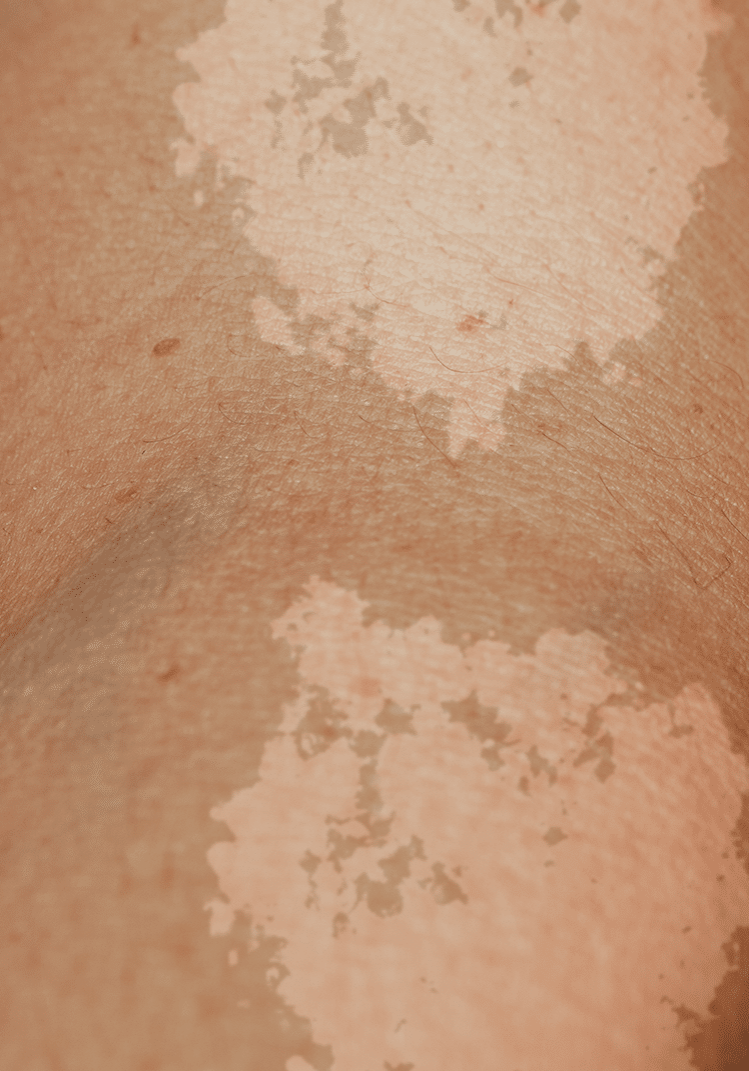
What is Tinea Versicolor (Sun Fungus)?
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, a type of fungus that naturally resides on the skin. This overgrowth disrupts the skin's pigmentation, resulting in discolored patches that can be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. These patches often appear on the chest, back, and neck, and are not typically itchy. The infection is not considered contagious.
What are the symptoms of tinea versicolor?
-
Variable coloration
Patches can be lighter (hypopigmentation) or darker (hyperpigmentation) than the surrounding skin, and may appear pink, tan, or brown. This color variation is where the name "versicolor" originates.
-
Location
Typically affects the trunk, neck, and upper arms, but can occur on other areas of the body.
-
Scaling
Patches often have a fine, powdery scale.
-
Environmental factors
Hot, humid climates, excessive sweating, and oily skin can create an environment conducive to Malassezia overgrowth.
-
Not contagious
It is important to note that although this is a fungal infection, it is not considered contagious. The overgrowth of the yeast is what causes the skin discoloration.
How to prevent tinea versicolor?
Because Malassezia yeast is a normal resident of the skin, complete prevention can be challenging. However, certain measures can help minimize the risk of overgrowth:
Maintain good hygiene: Regular washing of the skin can help control yeast levels.
Control sweating: Wear breathable clothing, especially in hot, humid weather.
Use anti-fungal washes: Regular use of anti-fungal shampoos or washes, particularly during warm months, may help prevent recurrence.
Minimize Oil: Avoid excessive use of oily skin products.
Treatment options for tinea versicolor?
Topical anti-fungal medications: These are often the first line of treatment and include creams, lotions, and shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or clotrimazole. These medications work by inhibiting the growth of the fungus.
Oral anti-fungal medications: In more severe or widespread cases, or when topical treatments are ineffective, oral anti-fungal medications such as fluconazole or itraconazole may be prescribed.
Maintenance therapy: Because tinea versicolor has a tendency to recur, maintenance therapy with topical or oral anti-fungals may be recommended, especially for individuals living in warm, humid climates.
It is important to understand that even after the infection is treated, the skin discolouration may take weeks or even months to return to its normal color.
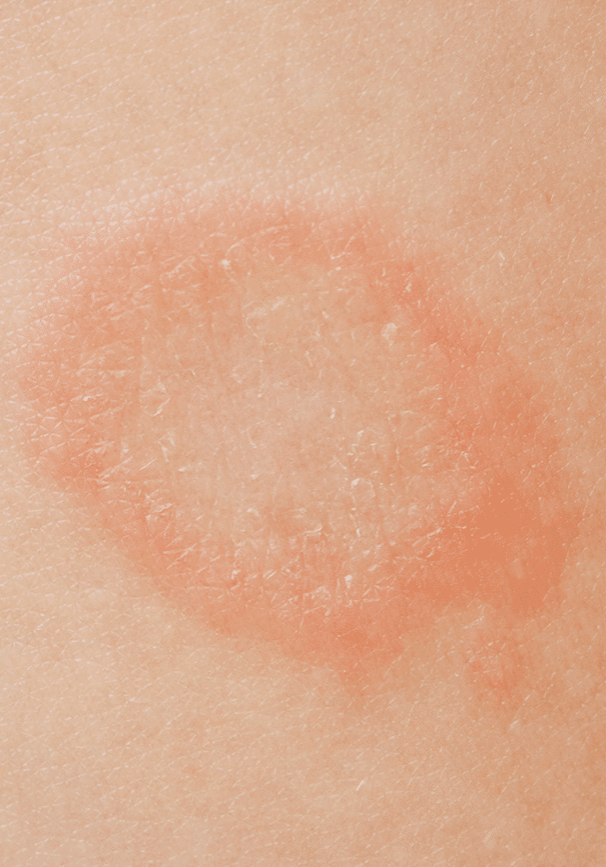
What is Tinea Corporis (Ringworm)?
What are the symptoms of ringworm?
-
Ring-shaped lesions
The classic presentation is a circular or oval patch of skin with a raised, scaly border and a clearer center, giving it the "ringworm" appearance. However, it's crucial to emphasize that this infection is caused by a fungus, not a worm.
-
Itching
The affected area is often intensely itchy.
-
Scaling & redness
The skin within the ring is typically scaly and red or inflamed.
-
Variable appearance
The size and appearance of the lesions can vary, and multiple rings may appear.
-
Contagious
Tinea corporis is contagious and can be spread. Transmission can occur through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal, contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, and contact with infected soil, though this is less common.
How to prevent ringworm?
Preventing tinea corporis involves minimizing exposure to the fungus and practicing good hygiene:
Practice good hygiene: Regularly wash hands and body, especially after contact sports or handling animals.
Avoid contact with infected individuals or animals: Do not share personal items like towels, clothing, or combs.
Keep skin clean and dry: Dry skin thoroughly, especially after sweating or showering.
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight clothing can create a warm, moist environment that promotes fungal growth.
Clean and disinfect: Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces in gyms, locker rooms, and other public areas.
Inspect pets: If you have pets, have them checked by a veterinarian for fungal infections.
Treatment options for ringworm?
Topical anti-fungal medications: These are often the first line of treatment and include creams, lotions, and shampoos containing Treatment aims to eliminate the fungal infection and relieve symptoms:
Topical anti-fungal medications: These are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate cases. Common over-the-counter and prescription anti-fungal creams, ointments, and lotions contain ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, ketoconazole, or terbinafine. Treatment typically lasts for several weeks, even after symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the fungus.
Oral anti-fungal medications: For severe or widespread infections, or when topical treatments are ineffective, oral anti-fungal medications like terbinafine, fluconazole, or itraconazole may be prescribed. These medications are typically taken for several weeks.
Hygiene practices:
Maintaining good hygiene is essential during and after treatment to prevent recurrence.
What is Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)?
What are the symptoms of jock itch?

-
Location
Typically occurs in the warm, moist areas of the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks.
-
Itchy rash
Characterized by an intensely itchy, red or reddish-brown rash.
-
Scaly boarder
The rash often has a raised, scaly border.
-
Discomfort
Can cause significant discomfort, including burning and stinging sensations.
-
Contributing factors
Excessive sweating, wearing tight-fitting clothing, warm & humid environments, obesity, and a weakened immune system.
-
Transmission
Jock itch is contagious and can be spread. Transmission is possible through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person and sharing contaminated towels, clothing, or other personal items.
It is also common for people with athletes foot to also contract Jock itch, because the same fungus is the cause of both conditions.
How to prevent jock itch?
Preventing jock itch involves keeping the groin area clean and dry:
Practice good hygiene: Wash the groin area daily with soap and water, and dry it thoroughly.
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Avoid tight-fitting clothing that can trap moisture. Opt for breathable fabrics like cotton.
Dry thoroughly: Pay close attention to drying the groin area after showering or exercising.
Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, clothing, or other personal items.
Manage sweating: If you sweat excessively, consider using absorbent powders or moisture-wicking underwear.
Treatment options for jock itch?
Topical antifungal medications: Over-the-counter anti-fungal creams, ointments, or powders containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine are often effective. Apply the medication to the affected area and the surrounding skin, following the product instructions.
Prescription anti-fungal medications: In severe or persistent cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger prescription-strength topical or oral anti-fungal medications.
Hygiene practices: Maintaining good hygiene is essential during and after treatment to prevent recurrence.
Your Tinea experts
By recognizing the diverse faces of tinea, practicing preventative measures like good hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items, and seeking prompt treatment, you can effectively combat these fungal foes and maintain healthy, radiant skin. Remember, knowledge is power, and with the right tools, you can conquer any fungal invader that dares to attack your skin's kingdom!