What is Vitiligo? Can Vitiligo go away?

Post written by: Carrie Jackman, PA-C
What is Vitiligo?
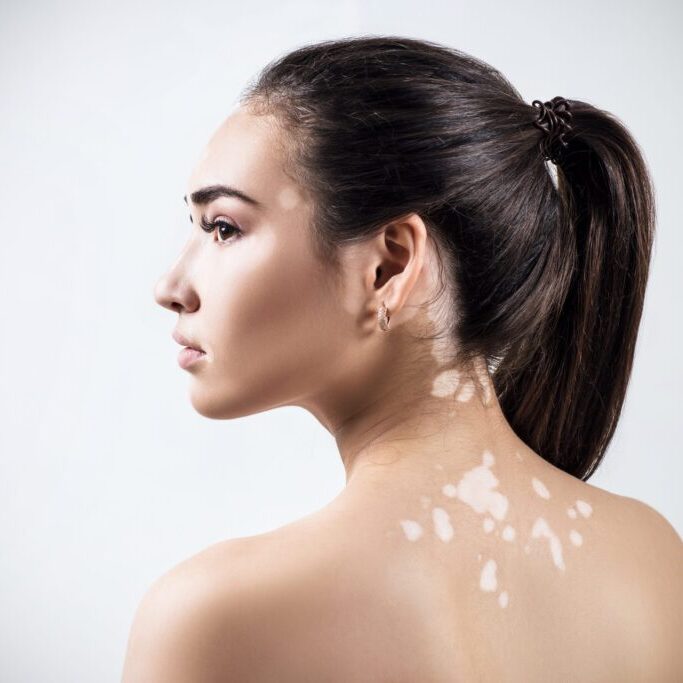
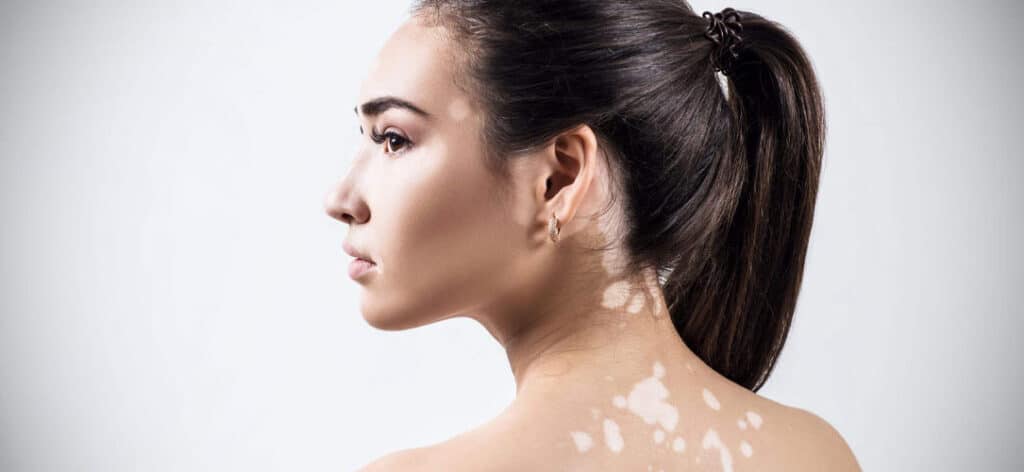
Vitiligo is a disease due to a lack of melanin that causes loss of skin color and develops white patches on your skin. The discolored areas typically get more extensive over some time and can affect any part of your body. It’s most common on the face, neck, and hands, but it can also affect your hair and the inside of your mouth.
The color of your skin and hair is determined by melanin. Vitiligo occurs when the cells producing melanin die or stop functioning. Although the symptoms appear to all skin types, it is more apparent to darker skin color. This condition isn’t life-threatening. However, it can be stressful for people suffering from this.
Vitiligo treatment may restore the color to the affected area, but it doesn’t prevent a recurrence.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
These are the areas of your skin that are most commonly affected by Vitiligo.
- Mouth and eyes
- Fingers and wrists
- Armpits
- Groin
- Genitals
- Hair
- Inside your mouth
The area that Vitiligo may affect depends on the type of Vitiligo you have.
- Universal Vitiligo may affect nearly all skin surfaces.
- With Generalized Vitiligo, the discolored patches typically have the same progress as the corresponding parts (symmetrically)
- Segmental Vitiligo may affect only one side or part of your body and tends to occur at a younger age. It may progress for 1 to 2 years, then eventually stop.
- Localized Vitiligo may affect one or only a few areas of your body.
- Acrofacial Vitiligo may affect the face and hands and body openings such as eyes, nose, and ears.
Here are some common symptoms of Vitiligo.
- Patchy loss of skin color. This typically appears on the hands, face, and areas around body openings such as genitals, eyes, nose, and ears.
- Producing white or grey hair on the scalp, eyebrow, and skin
- Loss of color in the mucous membranes (thin and soft line tissues inside of your mouth and nose)
Anyone of any age can experience Vitiligo, but it usually occurs at 30 years old.
Types of Vitiligo
There are two main types of Vitiligo — segmental and nonsegmental Vitiligo. Universal or complete vitiligo is a rare case of Vitiligo when it can affect a person’s whole body.
Nonsegmental Vitiligo
In nonsegmental vitiligo, also known as generalized vitiligo, the signs usually appear on both sides of your body as symmetrical white patches.
These symmetrical white patches may appear on the:
- Back of your hands and arms
- The skin around body openings such as eyes, nose, and ears
- The knees
- The elbows
- The extremities
Non-segmental vitiligo is the most common type of vitiligo. It can affect 9 out of 10 people.
Segmental Vitiligo
Segmental vitiligo, also known as localized vitiligo, the white patches only affect one area of your body. This type of vitiligo is less common than nonsegmental vitiligo, but it’s a common condition in children. It affects 3 out of 10 children with vitiligo.
What causes Vitiligo?
As mentioned earlier, vitiligo is due to the lack of pigment called melanin in your skin. This condition causes white patches to develop on your skin or hair. Melanin is naturally produced by skin cells called melanocytes, and it plays the role of giving your skin its color.
It’s not yet clear why the melanocytes disappear from the affected areas of your skin. However, it may be related to these factors.
1. Autoimmune Conditions
Non-segmental vitiligo is thought to be an autoimmune condition. In an autoimmune disorder, the immune system isn’t functioning correctly. Instead of attacking viruses, your immune system will attack your body’s healthy cells and tissue. If you have nonsegmental vitiligo, your immune system attacks and destroys the melanocyte skin cells that are responsible for the production of melanin.
2. Risk Factors
You are most likely to be prone to nonsegmental vitiligo if:
- The condition runs through the family (mean other family members have it)
- Another autoimmune condition develops in the family. For example, if one of your immediate family has pernicious anemia.
- You have a history of another autoimmune condition.
- You have a type of skin cancer called Melanoma or cancer of the lymphatic system called non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Changes in your genes happened that are mainly known to be linked to nonsegmental vitiligo.
3. Neurochemicals
Segmental vitiligo is caused by the chemicals released from the nerve endings in your skin, which are poisonous to melanocyte skin cells.
4. Triggers
There is a chance that some particular events may trigger vitiligo. These include:
- Childbirth or other stressful event or changes in the body
- Skin damage or severe sunburn or cuts
- Exposure to certain harmful chemicals
An infection does not cause vitiligo. You cannot get it from someone else who has it.
Can Vitiligo go away?
If vitiligo is severe and it’s making you unhappy, you may want to consider treatments. The white patches developed on your skin caused by vitiligo are often permanent. However, there are treatments available that can help in reducing their appearance.
If the patches are small, you can try applying skin camouflage cream to cover them up. You can also use steroid creams to restore some lost pigment. However, long-term use of this can cause stretch marks and thin skin, so other alternatives may use other topical medications to prevent this. Light therapy can also be beneficial to some vitiligo patients. Although treatment for Vitiligo is tough, there may be some options that are right for you.
To learn more about Vitiligo, visit Smart Skin Dermatology and see all the services that we offer. Schedule your consultation and contact us today!
About the Author

Carrie Jackman, PA-C, brings a unique blend of expertise, passion, and genuine care to Smart Skin Dermatology. Carrie’s passion extends beyond treating specific conditions. She thrives on building relationships with her patients, providing a warm and welcoming environment where everyone feels comfortable and heard. Her genuine care shines through in her interactions, ensuring each patient receives personalized attention and understanding. Read full bio.